Rhenium, a rare and valuable metal, is crucial in high-performance applications, particularly within the aviation and energy industries. Known for its heat resistance and strength, rhenium is often found in alloys like nickel-based superalloys used in aircraft turbines and energy sector equipment. However, its scarcity makes it essential to recycle rhenium from scrap sources such as sputtering targets, rods, and sintered residues. Recycling rhenium not only reduces environmental impact but also ensures a sustainable supply chain for industries that rely on this critical material.
This article explores key sources of rhenium scrap, the industries that generate these materials, and why companies need to partner with professional recyclers to optimize the value of their rhenium waste.
1. Key Sources of Rhenium Scrap
Several industrial byproducts contain valuable amounts of rhenium that can be recycled. Here are the most common sources:
-
Pellets and Sputtering Targets: Rhenium is used in sputtering targets for coating processes in electronics and aerospace components. These targets often degrade after multiple uses, becoming a valuable source of rhenium scrap. The residual material can be efficiently recycled to recover rhenium for reuse in manufacturing.
-
Punching Waste and Sheet Metal: The production of aerospace components and energy systems often results in waste metal from cutting and punching operations. Rhenium-containing alloys like nickel-based superalloys (Ni-Re) are used in high-temperature environments, making their residual scrap ideal for recycling.
-
Rods and Sinter Residues: During the production of high-performance components, sintered rhenium alloys may result in leftover material in the form of rods or residues. These materials often contain significant rhenium content and are prime candidates for recycling processes.
-
Rhenium Alloys: A variety of alloys contain rhenium, particularly in high-stress environments such as aviation turbine blades and combustion chambers. These alloys, once they reach the end of their life cycle, provide an important source of rhenium scrap.
-
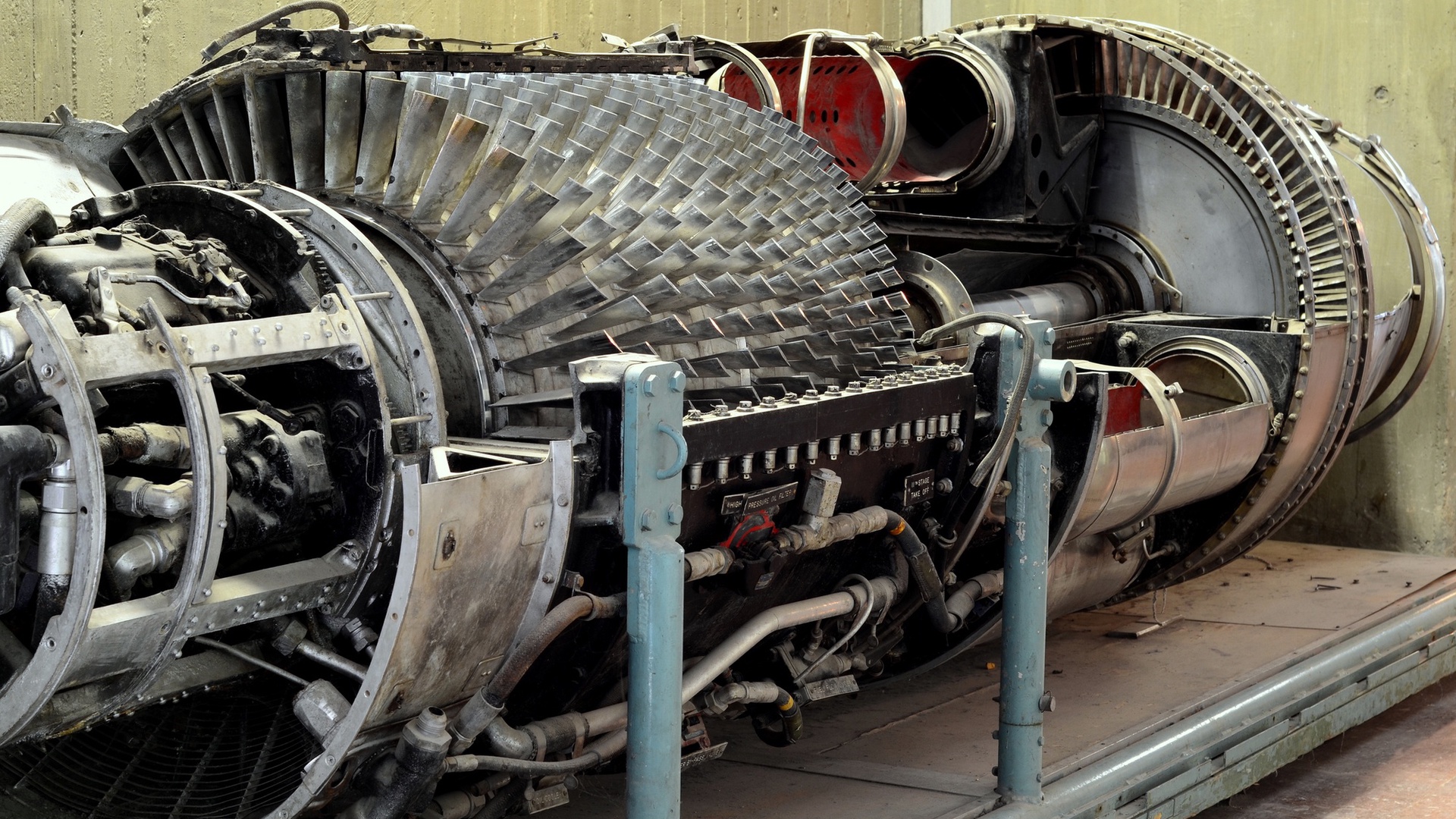
Nickel-Based Alloys Containing Rhenium (Superalloys): The aviation industry, in particular, uses nickel-based superalloys with rhenium to withstand extreme temperatures in jet engines. These superalloys often include 3-6% rhenium, making turbine blades, vanes, and other engine components excellent sources of recyclable rhenium.
-
Tungsten-Rhenium (WRe) and Molybdenum-Rhenium (MoRe) Materials: Both tungsten-rhenium and molybdenum-rhenium alloys are used in applications where high heat tolerance is essential, such as in thermocouples, x-ray tubes, and electrical contacts. These materials, after being replaced or scrapped, contain significant quantities of rhenium that can be recovered through specialized recycling processes.
2. Industries Producing Rhenium Scrap
Rhenium is a vital component in various industries that require materials capable of withstanding extreme conditions. The following sectors are key sources of rhenium scrap:
-
Aviation Industry: The aerospace industry is the largest consumer of rhenium-containing superalloys. Turbine blades and combustion chamber components often contain rhenium for its ability to maintain structural integrity at high temperatures. Once these parts are decommissioned, they become valuable scrap material. The demand for rhenium in aviation is driven by the need for lightweight, high-strength alloys that increase fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
-
Energy Sector: Power generation, especially in gas turbines, relies on high-temperature superalloys that often contain rhenium. Once parts like turbine blades or combustion systems are retired, energy facilities are a significant source of rhenium scrap. The drive for more efficient, cleaner energy has only increased the demand for high-performance rhenium alloys in this sector.
-
Electronics and Medical Devices: Rhenium is used in a variety of specialized electronics and medical devices, including x-ray tubes, where its high melting point and heat resistance are critical. The scrap generated from the production or disposal of these devices can be a source of valuable rhenium for recycling.
3. Why Recycle Rhenium?
Given rhenium’s rarity and the high cost of mining and refining the metal, recycling provides a cost-effective and sustainable solution. There are several reasons why companies involved in aviation, energy, and manufacturing should consider recycling their rhenium scrap:
-
Economic Value: Rhenium is one of the most expensive metals due to its scarcity. Recycling allows companies to recapture this value from scrap materials, turning waste into a revenue stream. Recycled rhenium can be reintroduced into the supply chain, reducing dependence on primary rhenium mining.
-
Sustainability: Mining rhenium is an energy-intensive process that has significant environmental impacts. By recycling rhenium-containing scrap, companies reduce the need for new mining, lowering their carbon footprint and contributing to a more sustainable manufacturing process.
-
Supply Chain Stability: The demand for rhenium is only expected to grow, particularly in the aviation and energy sectors. Recycling helps ensure a stable supply of rhenium, reducing vulnerability to market fluctuations and geopolitical risks associated with sourcing raw materials.
4. How to Maximize Returns from Rhenium Scrap
To maximize the value of rhenium scrap, companies need to partner with specialized metal recycling firms that have the expertise and equipment to efficiently recover rhenium from a variety of alloys and scrap forms. When selecting a recycler, consider the following:
-
Recycling Capabilities: Ensure the recycler has experience in processing rhenium-containing materials, such as superalloys, sputtering targets, and sintered residues. Advanced techniques like hydrometallurgy or pyrometallurgy are often required to efficiently extract rhenium from scrap.
-
Compliance and Certifications: Select a recycling partner that follows environmental regulations and industry standards, ensuring that your company meets its sustainability goals. Look for certifications like ISO 14001 (environmental management) to confirm that the recycler adheres to best practices.
-
Competitive Pricing: Work with a recycler who offers fair market value for your scrap, considering the high price of rhenium. Transparent pricing models and competitive offers are essential for maximizing returns.
Conclusion
Rhenium scrap represents a valuable resource for industries that rely on high-performance alloys, especially in the aviation and energy sectors. Companies producing rhenium-containing waste, such as pellets, rods, and superalloys, should consider recycling as a cost-effective and environmentally responsible option. Partnering with an experienced rhenium recycler not only allows companies to recover valuable metal but also supports a more sustainable future.
Ready to recycle your rhenium scrap? Contact Quest Metals today to learn more about how we can help you maximize the value of your rhenium-containing waste.
References:
- U.S. Geological Survey. (2023). Mineral Commodity Summaries: Rhenium.
- European Commission. (2022). Critical Raw Materials for the EU: Rhenium.
- International Nickel Study Group (INSG). (2022). Nickel and Rhenium in Superalloys.